ZigBee Penetration Testing is rising, ZigBee Attacks can be disruptive to your entire network, learn how to secure your IoT network from malicious Hackers.
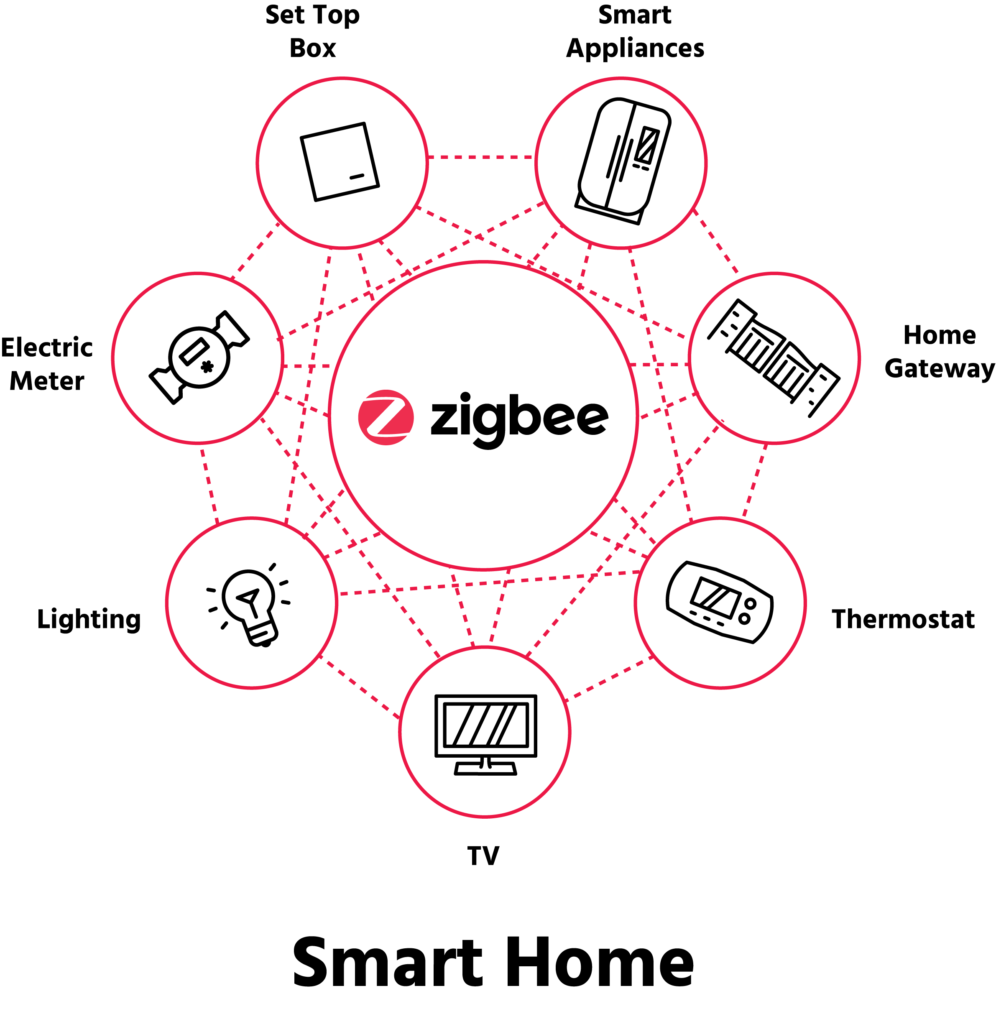
Zigbee is an open wireless technology that supports low-cost, and low-power devices to communicate effectively through a Wireless mesh network.
Table of Contents
WWWW – All devices connected
Typical application areas include:
- Home automation
- Wireless sensor networks
- Industrial control systems
- Embedded sensing
- Medical data collection
- Smoke and intruder warning
- Building automation
- Remote wireless microphone configuration

ZigBee Stack
ZigBee is a low-power, low-data-rate wireless communication technology. It is frequently used in smart lighting, home automation, and other Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
The ZigBee protocol specifies a set of layers that work together to provide devices with reliable communication.
ZigBee Physical Layer (PHY) – Layer 1
ZigBee networks are dedicated to sensor networks with low power consumption, they operate on 2.4 GHz ISM Frequency and have the standard IEEE 802.15.4 specification dedicated to radio signals.
It is responsible for transmitting and receiving data over the wireless channel. It handles tasks such as frequency selection, modulation, and signal encoding.
Some extra frequencies:
- 878Mhz – Europe
- 915 Mhz – America
- 745 Mhz – China
Channels
There are 16 channels available with 2 MHZ wide and 5 MHz between channels, a channel after is defined and used until the end of the communication.
ZigBee MAC Layer- Layer 2
This layer provides the interface between the network layer and the physical layer. It handles the transmission and reception of data and provides services such as security, acknowledgment, and error detection.
Frame Types:
- Data –
- Beacon –
- ACK –
- MAC –
- CRC –
ZigBee Network Layer (ZNL) – Layer 3
Provides the functionality to create and manage a ZigBee network. It handles the routing of messages between devices in the network and supports both mesh and star network topologies.
Physical Device types
Coordinator, Router, End Device
Network Device Types
FDD
RFD
Network Addresses
ZigBee Topologies
Star, Mesh, and Cluster tree
ZigBee Device Object (ZDO) Layer
This layer provides the interface between the application layer and the rest of the ZigBee stack. It handles device discovery, management, and network formation.
Application Layer
This is the topmost layer in the ZigBee stack. It defines the application-specific functionality and data structures that are exchanged between devices. It is responsible for handling device-specific operations such as sensor readings, device status updates, and control commands.
ZigBee Penetration Testing
- Physical
- Key
- Replay / Injection
Physical Attacks
PirateBUS and GoodFet help us find the encryption key by sniffing the transmission protocols or impersonation a device.
- 1-Wire
- JTAG
- SPI
- Async Serial
Key Based Attacks
ZigBee has two types of keys hardcoded (pre-shared-key) or updated by OTA.
Replay / Injection Attacks
ZigBee sniffer can be used to collect data
ZigBee Security Frameworks
KillerBee
ZigBee Hacking Hardware
- ApiMote
- ELK
- RZ Raven
Learn more about IoT Hacking – IoT Hacking 101




![[Top] Zigbee Protocol Analyzer: What you need to know](https://www.offensive-wireless.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Zigbee-Protocol-Analyzer-300x158.jpg)